 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Hellraisers Journal – Monday November 23, 1908
Report on Recent Legislation from the National Child Labor Committee
From the Duluth Labor World of November 21, 1908:
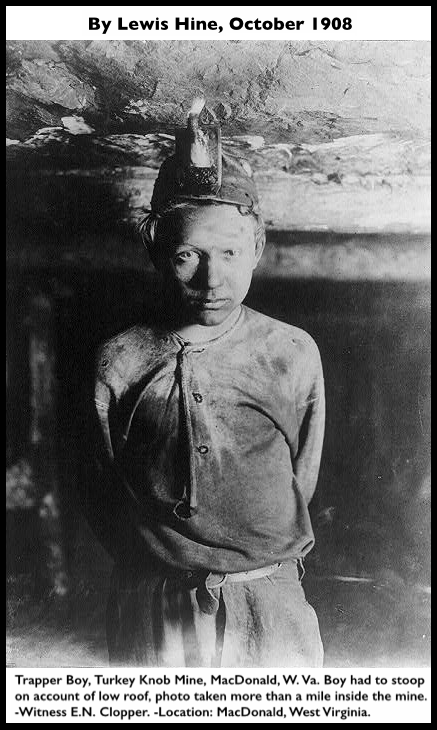
EFFORTS TO SUPPRESS CHILD LABOR EVILS
—–
Nine States Have Passed Remedial Measures
and Entire Country is Aroused.
—–
But Much Yet Remains to be Done
to Protect American Children.
—–Mr. A. J. McKelway, secretary of the National Child Labor Committee for the southern states has recently published a report of the years’ progress in child labor legislation, from which we glean the following excerpts.
Progress in 1908.
The year 1908 was an off year in state legislative sessions, as thirty-eight states have their legislatures meet in 1909. The national child labor committee reports progress in nine states, in addition to the passage of the District of Columbia child labor bill, which had been agitated for several years. This act of federal legislation was not all that was hoped for by the friends of the cause, as the pages of the senate, though not of the house, and the children of dependent parents are exempted from the operation of the law. In other respects the law approaches the standard of the more advanced states.
New York State.
An important amendment to the New York child labor law was the transferring of the enforcement of the mercantile child labor provisions from the local boards of health to the state labor department, and the provision for a bureau of mercantile inspection. This amendment was bitterly contested by interested parties and Governor Hughes sent two special messages to the legislature concerning the necessity of this change in the law.
New Jersey and Ohio.
In New Jersey, the effort to forbid night work for children under 16 years of age failed, but a compulsory education amendment requires children from 7 to 17 to attend school, except that children of 15 who are regularly employed are excused from such attendance.
In Ohio two efforts to weaken the child labor law failed and an eight-hour law was passed for boys at work under 16 and for girls under 18. This puts Ohio abreast of the most advanced states in this regard.






 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~


 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~

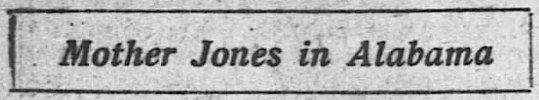
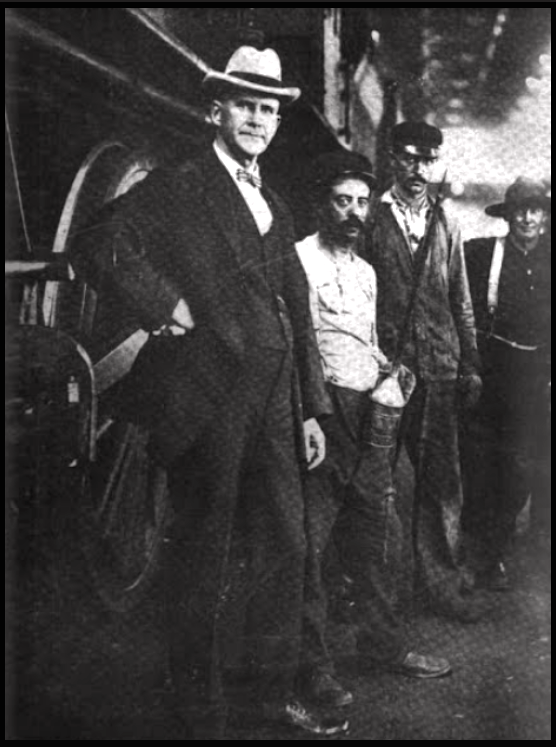
 T HAD been thirteen years since I bid farewell to the workers in Alabama and went forth to other fields to fight their bitter battles. I returned again in 1908 to see what they were doing for the welfare of their children. Governor Comer, being the chief star of the State, I went out to Avondale, on the out skirts of Birmingham, to take a glance at his slave pen. I found there some where between five and six hundred slaves. The governor, who in his generous nature could provide money for Jesus, reduced the wages of his slaves first 10 per cent, and then 16.
T HAD been thirteen years since I bid farewell to the workers in Alabama and went forth to other fields to fight their bitter battles. I returned again in 1908 to see what they were doing for the welfare of their children. Governor Comer, being the chief star of the State, I went out to Avondale, on the out skirts of Birmingham, to take a glance at his slave pen. I found there some where between five and six hundred slaves. The governor, who in his generous nature could provide money for Jesus, reduced the wages of his slaves first 10 per cent, and then 16. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
